8 Ways to Write Protect USB Drive: Quick Guide
5. Wenovo USB Disks Access Manager
USB Disks Access Manager is the simplest tool here to use with a single window and three options to choose from. By default the system will have both read and write access, this can be changed to read only preventing any data from being written. Or you can select disable to stop the device from showing up in Explorer by disabling the USB storage driver.
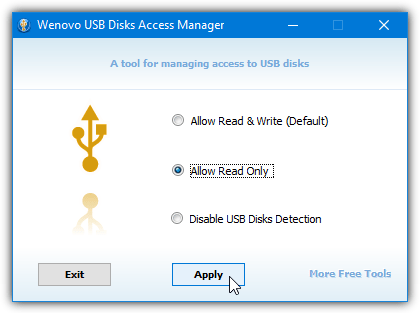
After the selection has been made press Apply and (re)insert any USB storage devices for the changes to take effect. Even though the program downloads with the word “setup” in its filename, it is actually a portable executable.
Download Wenovo USB Disks Access Manager
6. USB Flash Drives Control
This small piece of software is from developer Binisoft, which is now owned by security company Malwarebytes. The idea of USB Flash Drives Control is to be a more permanent solution that is always running because it installs as a system service and is controlled entirely from its tray icon context menu.
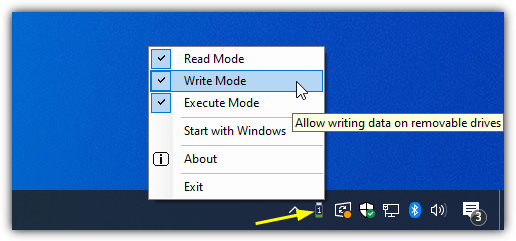
After install, you have three main options from the tray icon menu that are basically the same as the tools above. The first is Read Mode, disable it and USB drives will be unavailable on the system. Uncheck the Write Mode option to make all inserted USB drives read only. Turning off Execute Mode will stop any executable files from being launch on removable drives. As usual, changes take effect the next time the drive is inserted.
During uninstall, USB Flash Drives Control offers to reset the settings in the registry back to the system defaults. This is useful if you have been using any of these options here and just want to put the system back to the default settings.
Download USB Flash Drives Control
7. Disable USB Access Or Write Protect Drives By Editing The Registry
For the most part, the tools above disable or enable USB device write access through the system registry and one simple value change. Complete denial of access to the USB device is also another change to a different value.
We won’t cover manually editing the registry to write protect a USB drive here as it’s covered in another article. If you would like to know how to do it, read the article and the section on editing the registry yourself to enable write protection. Alternatively, download the ready made .REG files from below.
We’ve also covered how to disable removable storage devices such as USB drives by editing the registry elsewhere. Remember, attached USB storage devices will have to be reinserted for the changes to be applied. Download the .REG files from below.
Download DisableUSBMassStorage.reg
Download EnableUSBMassStorage.reg
Just download the file you want and double click it to import the data into your registry. Obviously, these are more manual options to a more friendly user interface but they do the same job in the background.
8. Write Protect A Single USB Device
The disadvantage the methods above have is the changes affect all devices attached to the system. All USB flash drives, memory cards, or hard drives will be write protected until the setting is changed to full access. This solution write protects only those drives you want on the local system, other systems will still have full access.
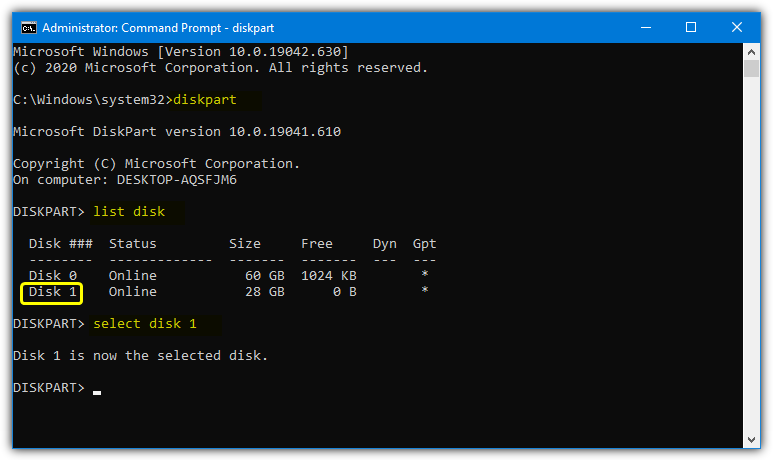
1. Open an admin Command Prompt (press Ctrl+Shift+Enter after typing cmd into Start) and type Diskpart.
2. Type List Disk to see the list of attached disks. Find the number corresponding to the USB storage device you want to write protect and enter Select Disk #.
3. Type Attributes disk set readonly, to confirm read only has been set you can optionally type attributes disk. If Read-only says Yes then it was successful and your drive is write protected on next insert.
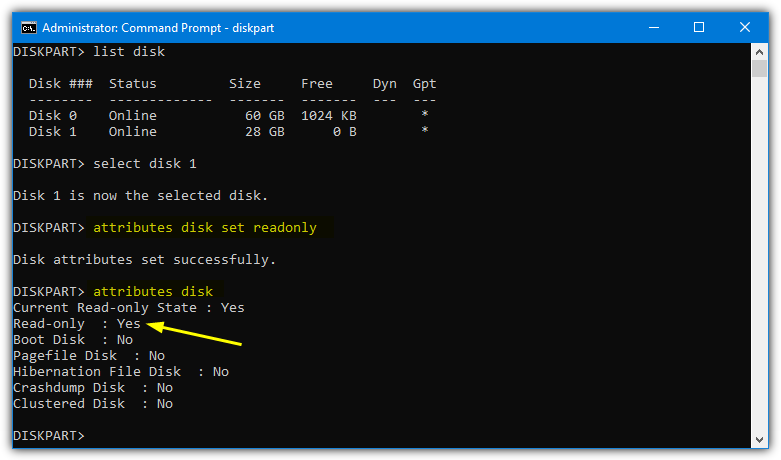
4. Type Exit and close the Command Prompt. To disable write protect for that drive enter Attributes disk clear readonly at step 3 instead.
This method is not a secure solution because the ID given to the device in the registry differs depending on which USB port it’s plugged into. Use another port and a new ID with a new write protect value will be created allowing full access. An obvious but inefficient workaround is attaching the drive to all available USB ports in turn and setting the write protect flag for each.
Tip: It’s possible to write protect a specific drive without using Diskpart and optionally create a .REG file to quickly turn the setting on or off. You do need to know the hardware name for the drive but it should be easy enough to work out from the list of USB devices. Go to the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum\USBSTOR
Find the drive name in question from the list and expand it to reveal a key with a unique ID, expand that also. Then go to Device Parameters > Partmgr. Changing the Attributes Value from 0 to 2 will make the drive read only on that specific USB port.
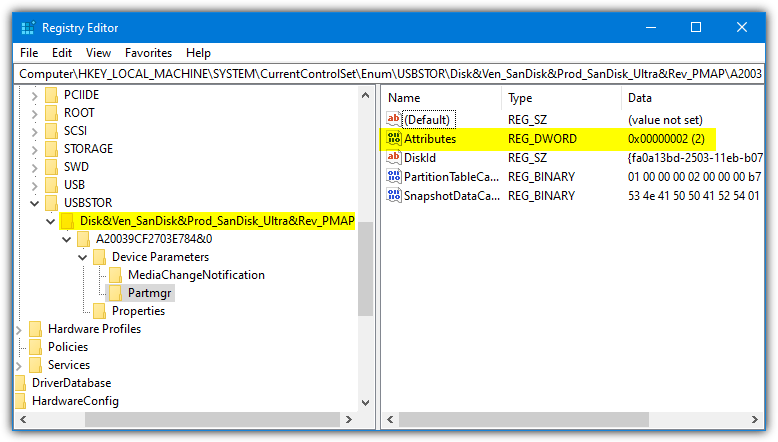
Right click on Partmgr and export the key with the Attributes value set to 0 and then 2. That will allow you to quickly click on either to change the status of the drive. Multiple unique IDs inside the device name key means it has been inserted into multiple USB ports and each one represents a different port. Change the Attributes value for each to protect the device in all used ports.

I guess I’ll be getting a drive with a hardware write protect switch then… There’s literally NO point whatsoever in making YOUR drive *read only on ONLY your own system. The point of making a drive READ ONLY would be so that when you’re using your drive on other PCs, it doesn’t “catch something”… You know, for when you come back home and ultimately plug it back into your own PC…
So if there is no way to physically lock the drive down, so that it’s READ ONLY on ANY and EVERY PC you connect it to,,, it’s futile…! Guess I’ll have to get one that has a hardware lock…!
Unless, there IS a way to lock a drive so that it is READ ONLY on ANY device you plug it in to… That’s what I NEED… Prime example is, I am about to take a “thumb drive” over to fed-ex kinkos to print something… While there my USB drive may “contract” a “virus”! Only to bring it home to MY own PC… So yes, it would be most needed to learn and know how to lock USB drives down from ANY device (PC) they’re inserted in to…
This article is quite clearly about locking USB drive access on your own system, and essentially the opposite of what you want to do. If you bring home a USB drive with a virus on it, the system can’t be infected.
There are various ways to “try” and lock down a drive using things like read-only files and filling up the free space so nothing else can get on the drive.
Failing that, you simply can’t write protect a drive on every machine and USB port you plug it into through software alone.
Is there any way to protect files from accidently being moved or deleted but still be able
to be opied to other folders? I’m talking specifically about ancestral photos. I want to keep a master folder of the photo files but fear accidently clicking on “cut” instead of “copy” when choosing a photo to add to a photo album. Thanks!
This is very nice thanks for the update it’s very informative.
I am looking for a means of adding a hardware switch to an existing USB external drive to be able to select write protect.
raymondcc (lower case)
The article is well written and illustrated. It pretty much explains what should and shouldn’t be attempted by someone based upon their level of experience and skill. My thought is: Use a second computer – to experiment on and learn. Not the computer you already have data, files, and documents secured on. That’s the mistake I made.
Normally when I plug in a sketchy USB drive I use virtual mode in Returnil.
nice..
thanks, i will try it..